指针 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {char * p = (char *)malloc (10 ); 'a' ;1 ) = 'b' ;2 ) = 'c' ;free (p);printf ("%s \n" ,p);
输出 abc
指针函数:带指针的函数 函数的返回值为指针类型
函数声明 : int* func(int x,int y)
指针函数调用
示例1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #include <stdio.h> char *getWord (char c) {switch (c) {case 'A' : return "Apple" ;case 'B' : return "Banana" ;case 'C' : return "Cat" ;case 'D' : return "Dog" ;default :return "None" ;int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {char input;printf ("please input a charactar:" );printf ("%c\n" ,input);printf ("%s\n" ,getWord(input));return 0 ;
运行结果
1 2 3 please input a charactar :A A Apple
输入A ,getWord()返回值为 Apple的首地址,printf(“%s\n),输出首地址所指向的值
示例2 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <stdio.h> char *getWord2 (char c) {char str1[] = "Apple" ;char str2[] = "Banana" ;char str3[] = "Cat" ;char str4[] = "Dog" ;char str5[] = "None" ;switch (c) {case 'A' : return str1;case 'B' : return str2;case 'C' : return str3;case 'D' : return str4;default :return str5;int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {char input;printf ("please input a charactar:" );printf ("%c\n" ,input);printf ("%s\n" ,getWord2(input));return 0 ;
注意: 不要返回局部变量的指针
例子2中,str1数组是局部变量,这个字符数组在子程序结束后,它对应的存储空间会被释放.
函数指针:指向函数的指针 指向函数起始地址的指针
函数指针的定义
函数指针的使用 fptr = func;
int x = fptr(5,8);
“%x “ 打印指针本身
示例
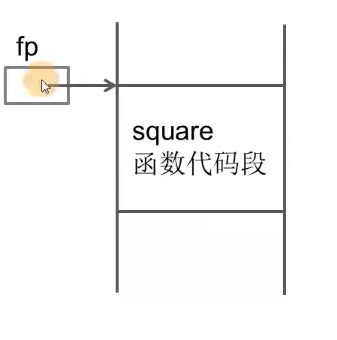
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 #include <stdio.h> int square (int num) {return num * num;int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {int num;int (*fp)(int ); printf ("please input a number:" );scanf ("%d" ,&num);printf ("fp = 0x%x, %d\n" ,fp,(*fp)(num)); printf ("fp = 0x%x, %d\n" ,fp,fp(num)); return 0 ;
square内存中占据的位置,fp保存square指针的入口地址,fp指向square(),*fp代表 调用square().
用法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 #include <stdio.h> int add (int num1,int num2) {return num1+num2;int sub (int num1,int num2) {return num1-num2;int calculate (int (*fp)(int ,int ),int num1,int num2) { return (*fp)(num1,num2);int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {printf ("3+5=%d\n" ,calculate(add,3 ,5 ));printf ("3-5=%d\n" ,calculate(sub,3 ,5 ));return 0 ;
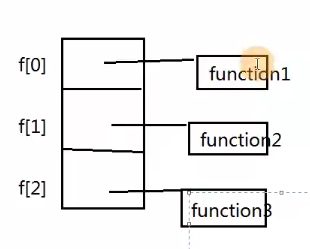
函数指针数组
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <stdio.h> void function1 (int ) ;void function2 (int ) ;void function3 (int ) ;void function1 (int choice) {printf ("input %d, run function1().\n " ,choice);void function2 (int choice) {printf ("input %d, run function2().\n " ,choice);void function3 (int choice) {printf ("input %d, run function3().\n " ,choice);#if (1) int main (int argc, const char * argv[]) {void (*f[3 ])(int ) = {function1,function2,function3};int choice;printf ("please enter a digit : [0-2]: " );scanf ("%d" ,&choice);while (choice>0 &&choice<3 ) {printf ("please enter a digit : [0-2]: " );scanf ("%d" ,&choice);printf ("run end" );#endif
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15J411Q7t9?from=search&seid=1110914330533311902
函数指针pft指向了一个已经声明的函数bar(),然后通过pft来实现输出字符和整型的目的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 void bar (char , int ) typedef void (*PFT) (char , int ) int main () pft ('e' ,91 );void bar (char ch,int i) " bar " <<ch<<' ' <<i<<endl;return ;
函数指针作为函数的参数,我们可以在一个函数的形参列表中传入一个函数指针, 然后便可以在这个函数中使用这个函数指针所指向的函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 typedef void (*PFT) (char , int ) void bar (char ch, int i) "bar " << ch << ' ' << i << endl;return ;void foo (char ch, int i, PFT pf) pf (ch, i);return ;int main () foo ('e' , 12 , pft);
函数对象
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 class A {public :int operator () (int x) return x; }int main () a (5 )<<endl;
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Func {public :int operator () (int a, int b) '+' << b << '=' << a + b << endl;return a;int addFunc (int a, int b, Func &func) func (a, b);return a;int main () addFunc (1 , 3 , func);
结构体 结构指针 point
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 struct point *pp ;struct point pt =400 ,600 };printf ("pt %d, %d \n" ,pt.x, pt.y);printf ("*pp %d, %d \n" ,(*pp).x, (*pp).y);printf ("pp-> %d, %d \n" ,pp->x, pp->y);
运行
1 2 3 pt 400, 600 600 600
结构指针的使用频度非常高,C语言提供了另一种简写方式,假定P指向一个结构的指针,可以用
p-> 结构成员 == *p.结构成员
代码表达式printf("origin is (%d,%d)\n", pp->x, pp->y);
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct rect r =200 ,300 },{400 ,500 }};struct rect *rp =printf ("pt1.x %d \n" ,r.pt1.x);printf ("(*rp).pt1.x %d \n" ,(*rp).pt1.x);printf (" rp->pt1.x %d \n" ,rp->pt1.x);printf ("r.pt1.x %d \n" ,r.pt1.x);
运行结果
1 2 3 4 pt1.x 200 .pt1 .x 200 .x 200 .pt1 .x 200
动态内存分配 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 int a[5 ] = {4 ,10 ,2 ,8 ,6 };int len;printf ("请输入你需要分配的数组的长度:len = " );scanf ("%d" ,&len);int *pArr = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) *len);5 ; 1 ] = 10 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <len ; ++i) {scanf ("%d" , &pArr[i]);for (int i = 0 ; i<len ; ++i) {printf ("%d\n " , *(pArr+i));free (pArr);
结构体变量(hao) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 #include <stdio.h> #include <memory.h> struct Student {int sid;char name[200 ];int age;void g (struct Student student) ;void g2 (struct Student *pst) ;void f (struct Student *pst) ;int main () {struct Student st =1000 , "张三" , 20 };printf ("%d %s %d\n" , st.sid, st.name, st.age);99 ;strcpy (st.name, "lili" );22 ;printf ("%d %s %d\n" , st.sid, st.name, st.age);struct Student *pst ;99 ; return 0 ;void g2 (struct Student *pst) {printf ("g2 %d %s %d\n" , pst->sid, pst->name, pst->age);void g (struct Student st) {printf ("g %d %s %d\n" , st.sid, st.name, st.age);
跨函数使用内存 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 #include <stdio.h> #include <malloc.h> struct Student {int sid;int age;struct Student *createStudent (void );void showStudent (struct Student *pst) int main () struct Student *ps;createStudent ();showStudent (ps);void showStudent (struct Student *pst) printf ("%d %d\n" ,pst->sid,pst->age);struct Student *createStudent () {struct Student *p = malloc (sizeof (struct Student)); 99 ;88 ;return p;
运算符优先级
算法 https://space.bilibili.com/501486236/video
typedef 别名 type_1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 typedef int ZHANGSAN;typedef struct Student {int sid;char name[100 ];char sex;int main (void ) {int i = 10 ; 20 ;printf ("%d\n" , j);struct Student st ;struct Student *ps =200 ;printf ("%d\n" ,st2.sid);
type_2
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 typedef struct Student {int sid;char name[100 ];char sex;int main (void ) {struct Student st ;99 ;printf ("%d\n" ,ps->sid);return 0 ;
type_3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 typedef struct Student {int sid;char name[100 ];char sex;int main (void ) {99 ;printf ("%d\n" ,ps->sid);return 0 ;
C++ 引用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 #include <iostream> using namespace std;void swap (int &x, int &y) int t = x;int main () int a = 3 , b = 4 ;"\t" << b << endl;swap (a, b);"\t" << b << endl;
函数模板 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 #include <iostream> using namespace std;template <typename T>T add (T x,T y) {return x+y;int main () #if 0 add <int >(5 ,3 )<<endl;add <double >(5.3 ,7.8 )<<endl;add <int >(4 ,6 )<<endl;add <string>("hello" ,"world" )<<endl;#else add (5 ,3 )<<endl;add (5.3 ,7.8 )<<endl;add (4 ,6 )<<endl;add ((double )5 ,7.8 )<<endl;#endif
swift语法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 var a = 10 var b: Int = 20 let aa = 40 if a< 20 {print ("a < 20 , true" )else {print ("a >= 20" )switch a {case 10 :print ("a equals 10" )case 20 :print ("a equals 20" )default :print ("other" )print ("Hello, World!" )for i in 25 ..< 100 {print ("aa,i=" ,i)var list = [1 ,2 ,3 ,4 ,5 ]for i in list{print ("aa, i=" ,i);var loop = 0 while loop< 10 {print ("loop, xxx = " ,loop)= loop + 1 func myFunc (a : Int ) -> Int {print ("this is a function" ,a)return avar mm = myFunc(a: 10 )print ("Hello, World!" ,a,b,aa,mm)
environmenthttps://juejin.im/post/5ad98412518825670960c13c
https://developer.android.com/ndk/