Data_Sort
排序
冒泡
1 | public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) { |
思路1:
第一次遍历最大的元素放到最右边,第二遍放倒数第二个位置,…
一开始的想法是i 也递增,j< arr.length - 1 - i 。但是这样可读性就不如 i 递减的方式,还要注意数组越界的问题,所以int i = arr.length - 1
思路2
还可以通过增加 swap,遍历后判断是否有序,当前一轮没有进行交换时,说明数组已经有序,没有必要再进行下一轮的循环了,直接退出
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17public static void bubbleSort2(int[] arr) {
boolean swap;
for (int i = arr.length - 1; i > 0; i--) { //剩余需要排序的长度
swap = false;
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int t = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = t;
swap = true;
}
}
if (!swap) {
break;
}
}
}
选择排序
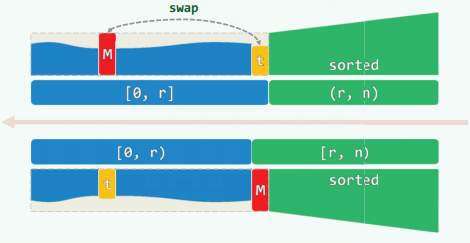
通过比较找到当前的最大元素M,并通过交换使值就位

1 | //选择排序 |
快速排序
思想: 前一序列的元素 都小于等于后一序列的元素,递归后 只剩单个元素时,自身就是有序的,可以作为递归基。
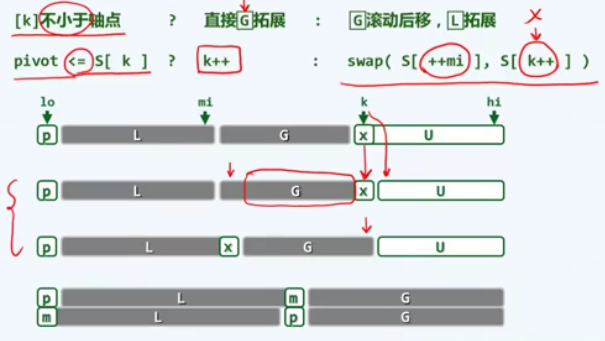
快速排序1
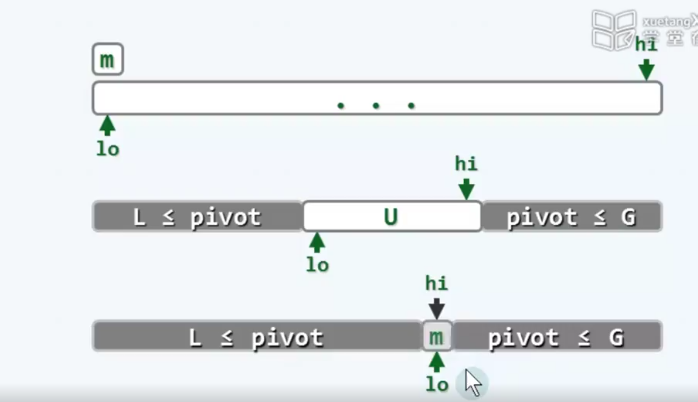
初始情况U是整个序列, L G是空,然后 lo hi都向内侧移动,最终hi lo指向同一个位置m,也就是最终的轴点。
L <= pivot <= G; U = [lo,hi]中,[lo]和[hi]交替空闲
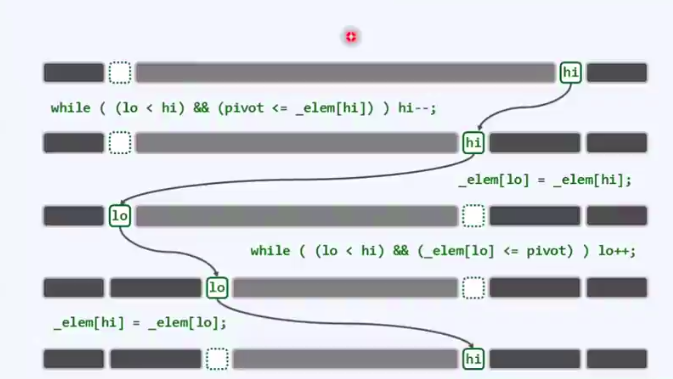
- 当_elem[hi]>pivot时,hi向左移动,自序列G跟着拓展。
- 当_elem[hi]<pivot时,把_elem[hi]移动到lo位置上。
- 向右移动lo,拓展子序列lo。
- 当elem[lo] > pivot时,把elem[lo] 移动到hi位置上。
- 最终hi lo指向同一个位置m,也就是最终的轴点pivot。
1 | public static void quickSort(int[] arr, int lo, int hi) { |
快速排序2
快速排序变种
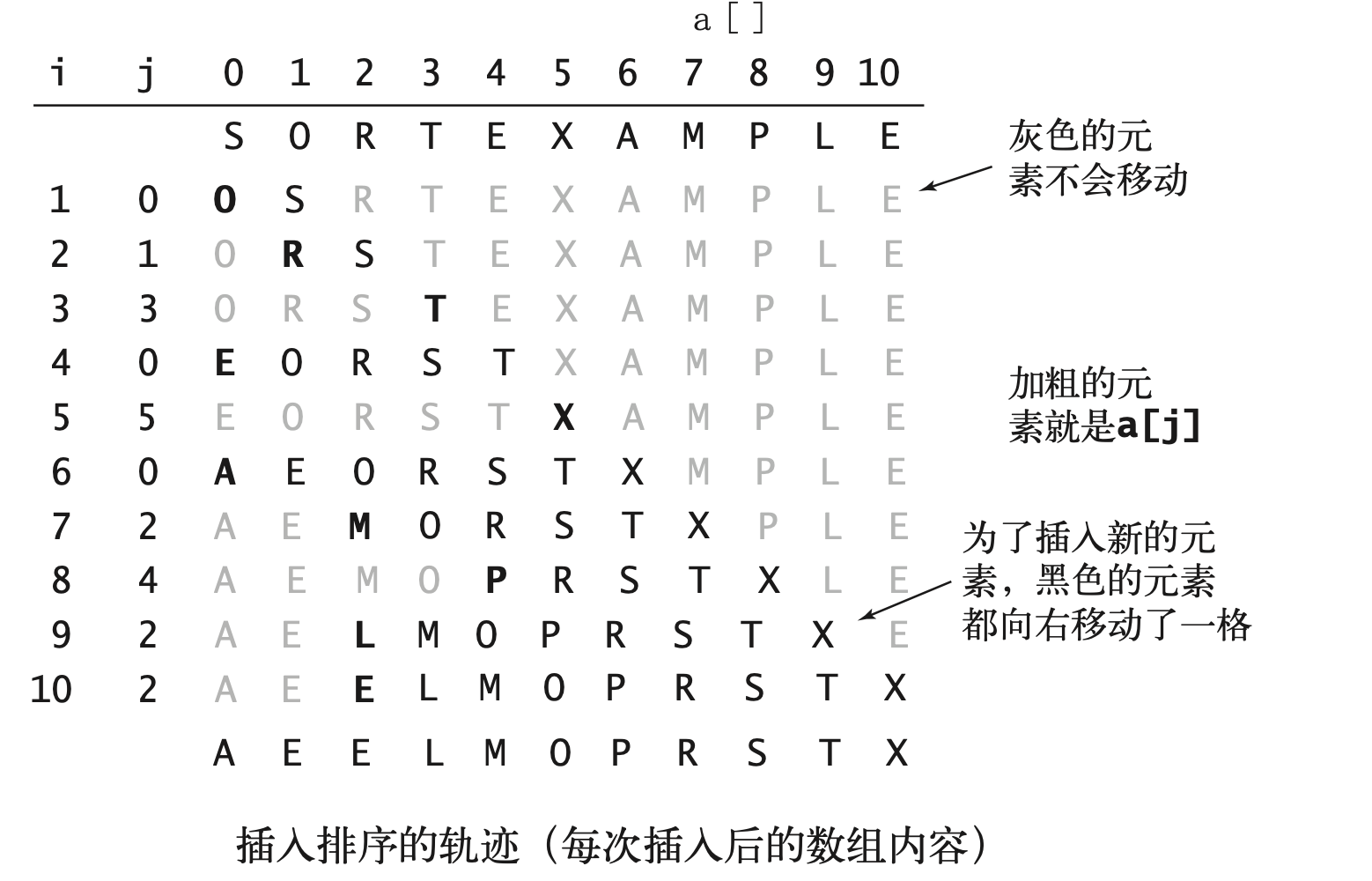
插入排序
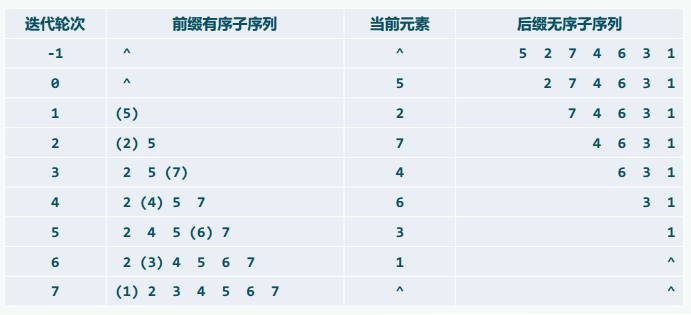
希尔排序

https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1LT4y137cK?from=search&seid=6852216660251002525
归并排序
代码不太理解(学堂在线)
符号表的各种实现的优缺点
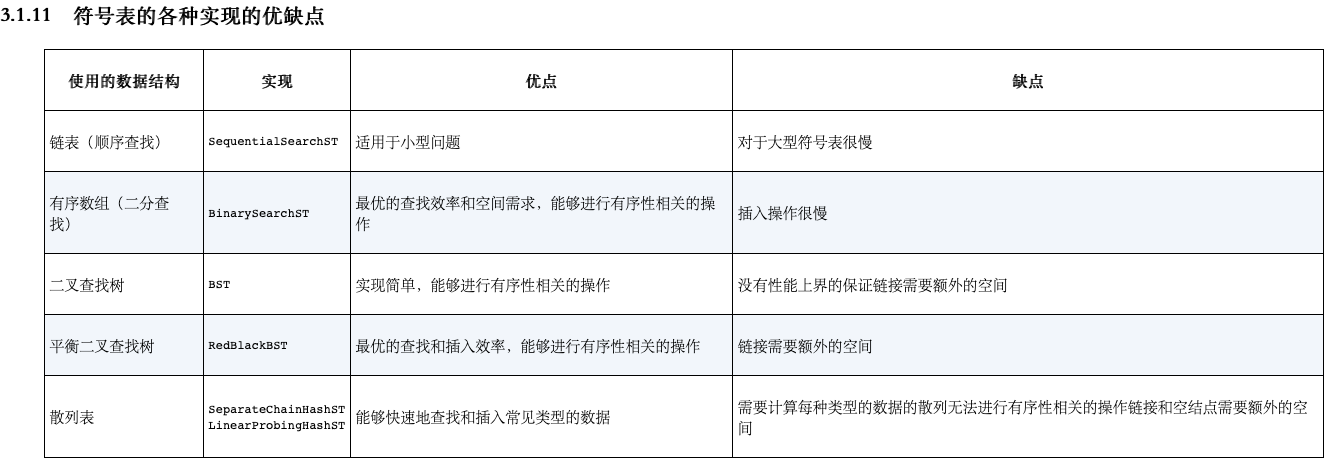
堆排序
自下而上
2 1 6 3 9 7 4 8 5
最末尾的内部节点所对应的秩开始 floor(9/2)-1=3,也就是第三个位置,接下来是堆6 1 2进行下滤操作
一开始很不理解为什么是 floor(9/2)-1,因为前面有 parent(i) = (i-1)>>1
其实这个9就是 arr.length,这里的 i是下标,也就是 arr.length-1,这样就很好理解为什么-1可以移出来
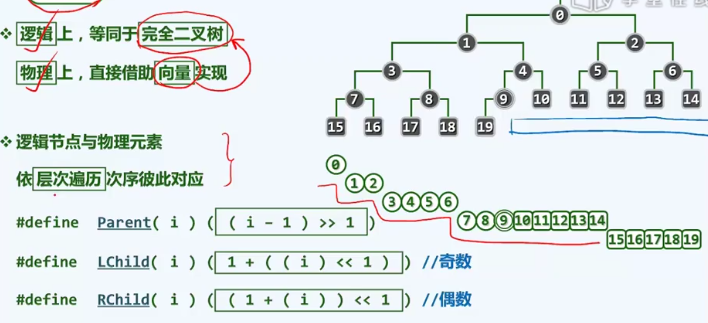
建堆
按照树的层序遍历顺序,从左到右开始建堆。
接着根据floyd算法开始调整, 5/2 - 1 = 1,第一个位置对应的是3,3上移
接着是5,上移, 上面左下图是调整之后的,完全二叉堆
上面的数字太小,https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WsNQuCa_-PU 这个视频有两次调整的情况
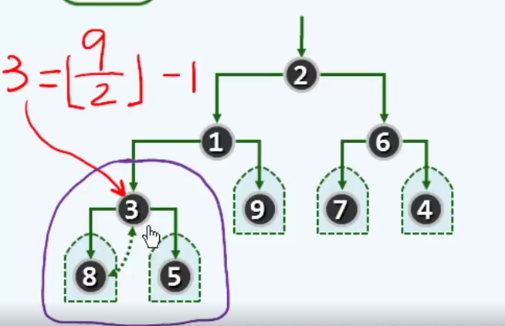
选取与调整
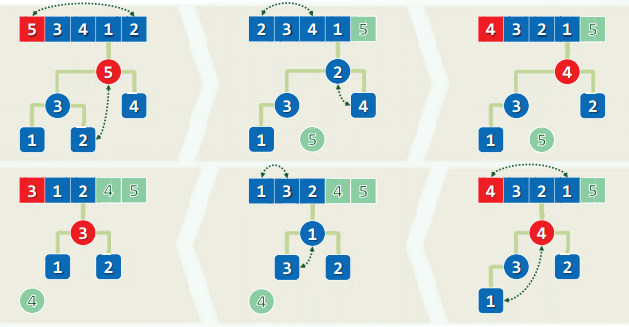
类似于选择排序
- 选取根节点5和末尾元素2交换,放到向量末尾,5放到 已排序序列,从完全二叉堆中移出。
- 对根节点2下滤
- 选取根节点4和末位置1交换,4放到已排序序列,下面依次操作
1 | public static void heapSort(int[] arr) { |