https://www.jianshu.com/p/8eb0623f08c6
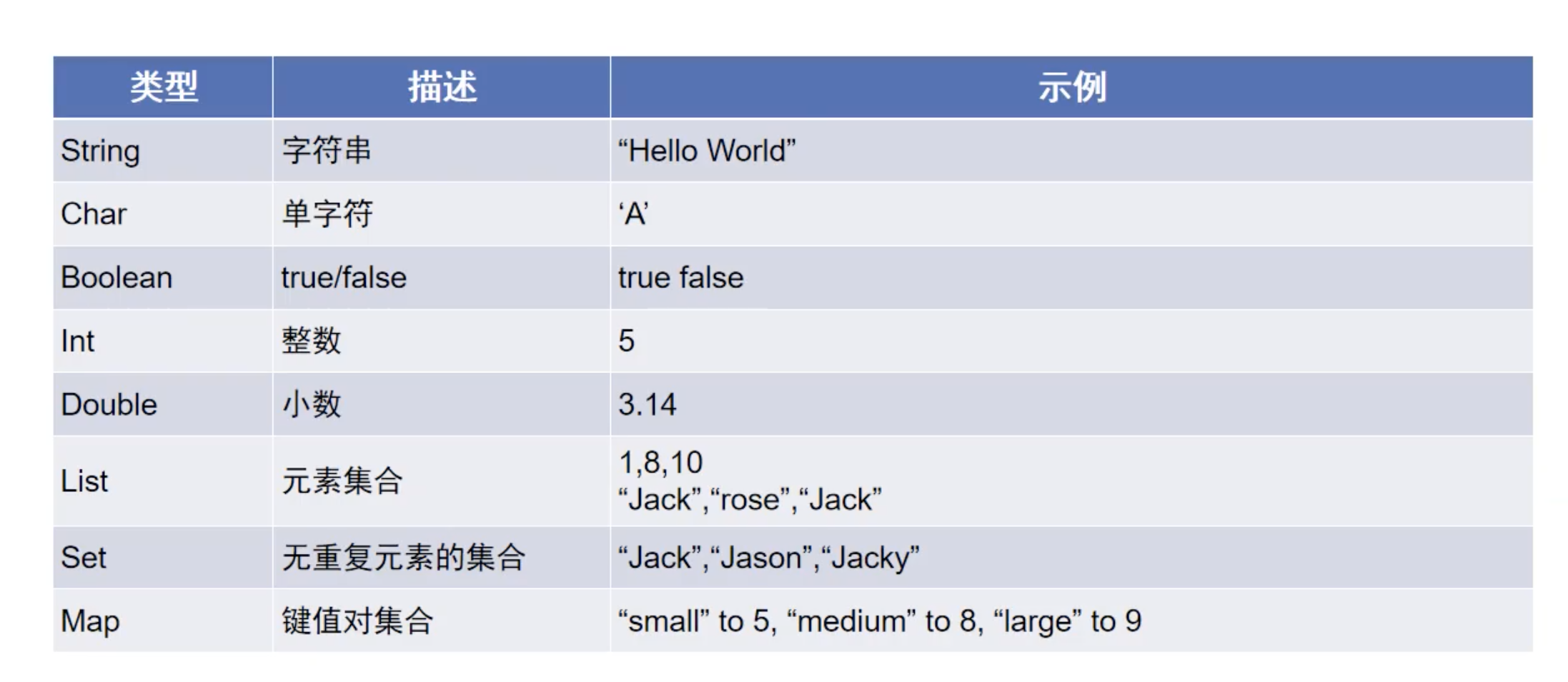
类型 Kotlin内置数据类型
类型推断 对于已经声明并赋值的变量,它允许你省略类型定义.
编译时常量 编译时常量只能再函数外定义,因为编译时常量必须在编译时赋值,而函数时在运行时才调用,函数内的变量也是在运行时赋值,编译时常量要在这些变量赋值前就已存在。
1 2 3 4 const val MAX =200 ;fun main () const val MAX =200 ; }
基本表达式 age表达式 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 val score = 6 ;if (score in 9. .10 ){ println("Big美女" ) }else if (score in 6. .8 ){ println("美女" ) }else { println("who knows" ) } if (score !in 1. .5 ){ println("good" ) }
美女
when 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 val school = "0小学" ;val level = when (school) { "幼儿园" -> "幼儿" "小学" -> "少儿" "中学" -> "青少年" else -> { "未知" } }
类似于 if else条件语句
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 var osd = when { isOdd() -> print("x is odd" ) isEven() -> print("y is even" ) else -> print("x+y is odd" ) } println("osd $osd " )
1 2 3 4 5 6 fun isOdd () Boolean { return false } fun isEven () Boolean { return false }
String模版 1 2 val flag = false println("Answer is : ${if (flag) "我可以" else "I can play" } " )
函数,函数参数 1 2 3 4 5 printUser("Jon" ) printUser(name = "john" ) fun printUser (name:String ,age:Int =2 ) println(name+age) }
Nothing类型 终止代码运行
反引号 `` 可以用来测试 某一段代码
1 2 3 fun `**~ special function with test util ~**`() }
Kotlin和Java保留不同的关键字,使用反引号括住函数名能避免任何冲突
1 2 3 4 5 public class KeyWordJava public static void is () System.out.println("is invoked" ); } }
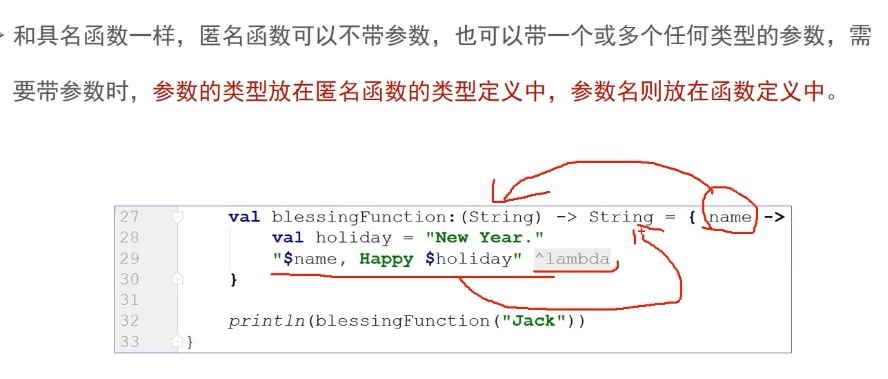
匿名函数 匿名函数可以当作变量赋值给函数类型变量。函数的类型,由传入的参数和返回值类型决定。
和具名函数不一样,除极少情况外,匿名函数不需要return关键字,来返回数据,匿名函数会隐式或自动返回函数体最后一行语句的结果。
通过匿名函数给标准函数 制定规则
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 val total = "Mississippi" .count()val totalS = "Mississippi" .count({letter-> letter =='s' }) println(total) println(totalS)
函数类型与隐式返回
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 val helloFunction:()->String helloFunction = { val greet = " how is going. " "hello girl , $greet " } val helloFunction1:()->String = { val greet = " how is going. " val hah = "haha" "hello beauty girl, $greet " } println(helloFunction()) println(helloFunction1())
hello girl , how is going.
匿名函数参数
1 2 3 4 5 val helloFunction2:(String)->String = {name-> val hah = "haha" "hello beauty girl, I am ${name} " } println(helloFunction2("Jon" ))
it关键字 定义只有一个参数的匿名函数时,可以用it来表示参数名。当需要传入两个值参,就不能用了。
1 2 3 4 5 val helloFunction3:(String)->String = { val hah = "haha" "hello beauty girl, I am ${it} " } println(helloFunction3("John" ))
类型推断 定义一个变量时,如果已把匿名函数作为变量赋值给它, 就不需要显示指明变量类型了。
1 2 3 4 5 val helloFunction4 = { val holiday = "New Year" "Happy $holiday " } println(helloFunction4())
类型推断也支持带参数的匿名函数,但为了帮助编译器更准确的推断变量类型,匿名函数的参数名和参数类型必须有。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 val helloFunction5:(String,Int ) -> String = {name,year -> val holiday = "New Year" "$name Happy $holiday $year " } println(helloFunction5("jon" ,2023 )) val helloFunction6 = {name:String,year:Int -> val holiday = "New Year" "$name Happy $holiday $year " } println(helloFunction6("jon" ,2023 ))
匿名函数成为lambda,将它的定义成为lambda表达式,它返回的数据成为lambda结果。
lambda由来:在定义匿名函数时,使用了lambda演算记法。
一个函数作为另一个函数的参数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 fun main () val disCountWord = { goodsName: String, hour: Int -> val currentYear = 2023 ; "${currentYear} 年, 双11 ${goodsName} 促销倒计时: $hour 小时" } showOnBoard("小玩具" , disCountWord) } fun showOnBoard (goodsName: String , getDiscountWords: (String , Int ) -> String ) val hour = (1. .24 ).shuffled().last(); print(getDiscountWords(goodsName, hour)) }
java实现传递函数 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public static void main (String[] args) showOnBoard("牙膏" ,((goodsName, hour) -> { int currentYear = 2023 ; return String.format("%s年,双11 %s 促销倒计时 %d小时 " ,currentYear,goodsName,hour); })); } public interface DiscountWords String getDiscountWords (String goodsName,int hour) ; } public static void showOnBoard (String goodsName,DiscountWords discountWords) int hour = new Random().nextInt(24 ); System.out.println(discountWords.getDiscountWords(goodsName,hour)); }
简略写法 如果一个函数的lambda函数排在最后,或者是唯一的参数,那么括住的lambda值参的一对圆括号就可以省略.
唯一的参数
AnonymousFunc2.kt
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 val totalS = "Mississippi" .count({letter-> letter =='s' }) val totalS1 = "Mississippi" .count{letter-> letter =='s' }
AnonymousFunc2.kt
排在最后,一对圆括号就可以省略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 showOnBoard("小玩具" , { goodsName: String, hour: Int -> val currentYear = 2023 ; "${currentYear} 年, 双11 ${goodsName} 促销倒计时: $hour 小时" }) showOnBoard("小玩具" ) { goodsName: String, hour: Int -> val currentYear = 2023 ; "${currentYear} 年, 双11 ${goodsName} 促销倒计时: $hour 小时" }
内联函数 类似于宏替换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 fun main () val disCountWord = ({ goodsName: String, hour: Int -> val currentYear = 2023 ; "${currentYear} 年, 双11 ${goodsName} 促销倒计时: $hour 小时" }) showOnBoard("小玩具" , disCountWord) } fun showOnBoard (goodsName: String , getDiscountWords: (String , Int ) -> String ) val hour = (1. .24 ).shuffled().last(); println(getDiscountWords(goodsName, hour)) }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public final class AnonymousFunc2Kt public static final void main () Function2 disCountWord = (Function2)null .INSTANCE; showOnBoard("小玩具" , disCountWord); } public static void main (String[] var0) main(); } public static final void showOnBoard (@NotNull String goodsName, @NotNull Function2 getDiscountWords) Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(goodsName, "goodsName" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(getDiscountWords, "getDiscountWords" ); byte var3 = 1 ; int hour = ((Number)CollectionsKt.last(CollectionsKt.shuffled((Iterable)(new IntRange(var3, 24 ))))).intValue(); Object var5 = getDiscountWords.invoke(goodsName, hour); boolean var4 = false ; System.out.println(var5); } }
内联后,代码直接替换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public final class AnonymousFunc2Kt public static final void main () Function2 disCountWord = (Function2)null .INSTANCE; String goodsName$iv = "小玩具" ; int $i$f$showOnBoard = false ; byte var3 = 1 ; int hour$iv = ((Number)CollectionsKt.last(CollectionsKt.shuffled((Iterable)(new IntRange(var3, 24 ))))).intValue(); Object var6 = disCountWord.invoke(goodsName$iv, hour$iv); boolean var5 = false ; System.out.println(var6); } public static void main (String[] var0) main(); } public static final void showOnBoard (@NotNull String goodsName, @NotNull Function2 getDiscountWords) int $i$f$showOnBoard = 0 ; Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(goodsName, "goodsName" ); Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(getDiscountWords, "getDiscountWords" ); byte var4 = 1 ; int hour = ((Number)CollectionsKt.last(CollectionsKt.shuffled((Iterable)(new IntRange(var4, 24 ))))).intValue(); Object var6 = getDiscountWords.invoke(goodsName, hour); boolean var5 = false ; System.out.println(var6); } }
函数引用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 fun main () showOnBoard("小玩具" ,::getDiscountWords) } private fun getDiscountWords (goodsName: String , hour: Int ) val currentYear = 2023 ; return "${currentYear} 年, 双11 ${goodsName} 促销倒计时: $hour 小时" } private fun showOnBoard (goodsName: String , getDiscountWords: (String , Int ) -> String ) val hour = (1. .24 ).shuffled().last(); println(getDiscountWords(goodsName, hour)) }
函数类型作为返回类型
函数类型也是有效的返回类型,也就是说可以定义一个能返回函数的函数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 fun main () val getDiscountWords = configDiscountWords() println(getDiscountWords("小玩具" )) } fun configDiscountWords () val currentYear = 2023 ; val hour = (1. .24 ).shuffled().last(); return { goodsName: String -> "${currentYear} 年, 双11 ${goodsName} 促销倒计时: $hour 小时" } }
闭包 作用: 控制作用域
匿名函数引用着定义自身函数里的变量
kotlin中的lambda就是闭包,上面
currentYear,hour 在configDiscountWords()中定义
{ goodsName: String -> “${currentYear}年, 双11 ${goodsName}促销倒计时: $hour 小时} 也在configDiscountWords()定义
2 引用了currentYear,hour变量. 所以形成闭包
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1wf4y1s7TG?p=34&spm_id_from=pageDriver
35 lambda与匿名内部类
java传递函数的方式
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public class JavaAnonymousClass public static void main (String[] args) showOnBoard("牙膏" , new DiscountWords() { @Override public String getDiscountWords (String goodsName, int hour) int currentYear = 2023 ; return String.format("%s年,双11 %s 促销倒计时 %d小时 " , currentYear, goodsName, hour); } }); } public interface DiscountWords String getDiscountWords (String goodsName, int hour) ; } public static void showOnBoard (String goodsName, DiscountWords discountWords) int hour = new Random().nextInt(24 ); System.out.println(discountWords.getDiscountWords(goodsName, hour)); } }
Null 编译时出错的方式,提前在编译期强迫开发者重视起来,而不是等到运行时报错。
? 变量为null,不会执行后面的方法
let匿名函数,返回lambda最后一行
可以支持函数链式调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 var str:String? = "butterfly" str = str?.let { if (it.isNotBlank()){ it.capitalize() }else { "butterfly" } } println(str)
!! 当变量为null,会抛出KotlinNullPointerException
空合并操作符 ?: 类似三目运算符
1 2 3 4 str=null str="guy" str = str?.let { it.capitalize()} ?:"butterfly" println(str ?: "girl" )
异常 执行之前,先进行检查,可以自定义异常
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 fun main () var number: Int ? = null try { checkOperation(number) number!!.plus(1 ) } catch (e: Exception) { println(e) } } fun checkOperation (number: Int ?) number ?: throw UnskilledException() } class UnskilledException : IllegalArgumentException "操作不当" )
先决条件函数 kotlin标准库 提供了一些便利函数,使用这些内置函数,可以跑出带自定义信息的异常,这些便利函数叫做先决条件函数。也可以用它定义先决条件,条件必须满足,目标代码才能执行。
1 2 3 4 fun checkOperation (number: Int ?) checkNotNull(number,{"Something is no good." }) }
字符串 String.kt
substring substring支持IntRange类型的参数,until创建的范围不包括上限值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 const val NAME ="Jimmy's friend" fun main () val index = NAME.indexOf('\'' ) NAME.substring(0 ,index) val str = NAME.substring(0 until index) println(str) }
spilt siilt返回的是List集合数据,List集合又支持解构语法特性,它允许你在一个表达式里给多个变量赋值,解构常用来简化变量的赋值。
1 2 3 val data = NAMES.split("," )val (girl1,girl2,girl3,girl4) = NAMES.split("," )println("$girl1 $girl2 $girl3 $girl4 " )
replcae 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 val str1 = "The people's Republic of China." val str2 = str1.replace(Regex("[aeiou]" )) { when (it.value) { "a" -> "8" "e" -> "6" "i" -> "9" "o" -> "1" "u" -> "3" else -> it.value } } println(str1) println(str2)
结果
The people’s Republic of China.
字符串的比较 用 == 检查两个字符串中的字符是否匹配, 用 === 检查两个变量是否指向内存堆上的同一对象, 而在Java中 ==做引用比较,做结构比较时用equals方法.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 val str3 = "Jason" val str4 = "Jason" println(str3==str4) println(str3===str4) val str5 = "jason" .capitalize() println(str3===str5)
结果
true
字符串遍历 1 2 3 str1.forEach { print("$it " ) }
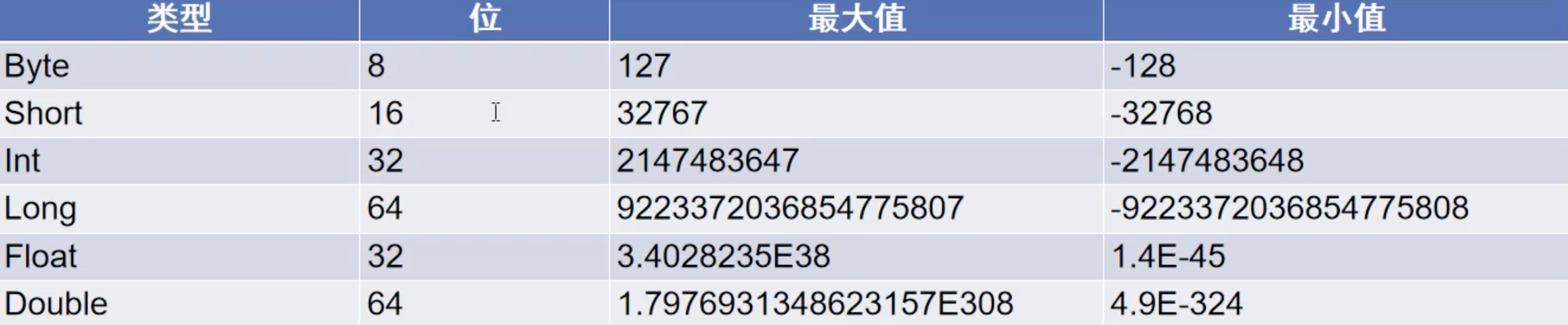
数字类型 kotlin所有的数字类型都是有符号的,也就是既可以表示正数,也可以表示负数。
安全转换函数 NumberConvert
toDoubleOrNull和toIntOrNull这样的安全转换函数,如果数值不能正确转换,与其触发异常不如干脆返回null值。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 val number1:Int ? = "6.66" .toIntOrNull() println(number1) println(8.956765 .toInt()) println(8.956765 .roundToInt()) val s = "%.2f" .format(8.956765 ) println(s)
结果
null
标准库函数 StandLibFunc.kt
apply apply函数可看作一个配置函数,传入一个接收者,然后调用一系列的函数来配置它以便使用,如果提供lambda给apply函数执行,它会返回配置好的接收者。
配置file对象,传入file对象配置它,配置完file对象返回.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 val file = File("E// I have a dream.txt" )file.setReadable(true ) file.setWritable(true ) file.setExecutable(false ) val file1 = File("E// I have a dream.txt" ).apply { setReadable(true ) setWritable(true ) setExecutable(false ) }
Lambda表达式里,apply能让每个配置函数都作用于接收者,这种行为又叫相关作用于,因为lambda表达式里的所有函数调用都是针对接收者的,或者说他们是针对接收者的隐式调用。
let let函数能是某个便利作用于lambda表达式里,让it关键字能引用它。let与apply比较,let会把接收者传给lambda,而apply什么都不传,匿名函数执行完,apply会发挥当前接收者,而let会返回lambda的最后一行。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 var result = listOf(3 , 2 , 1 ).first().let { it * it } println(formatGreeting(null )) println(formatGreeting("Jack" )) fun formatGreeting (guestNmae: String ?) return guestNmae?.let { "Welcom, $it " } ?: "What's your name" } fun formatGreeting2 (guestNmae: String ?) return if (guestNmae != null ) { "Welcom, $guestNmae " } else { "What's your name" } }
run
光看作用域行为, run和apply差不多,但与apply不同,run函数不返回接收者,run返回的是lambda结果.
run也能用来执行函数引用å
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 var file = File("THINKKOTLIN/I have a dream.txt" )val result = file.run { readText().contains("great" ) "xxx" } println(result) val result2 = "The people's Republic of china." .run(::isLong)println(result2) "The people's Republic of china." .run(::isLong) .run(::showMessage) .run(::println) fun isLong (name: String ) 10 fun showMessage (isLong: Boolean ) return if (isLong){ "Name is too long." }else { "Please rename." } }
with with函数是run的变体,他们的功能行为是一样的,但with的调用方式不同,调用with时需要值参作为其第一个参数传入。
1 2 var result3 = "The people's Republic of china." .run { length > 10 }val result4 = with("The people's Republic of china." ) { length >= 10 }
also also和let类似,和let一样,also也是把接收者作为值参传给lambda,但是有点不同: also返回接收者对象,而let返回lambda结果。因此also适合针对同一原始对象 ,利用副作用做事,肌肉also返回的是接收者对象,就可以基于原始接收者对象执行额外的链式调用 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 var fileContents: List<String>File(FILE_DREAM) .also { println(it.name) }.also { fileContents = it.readLines() } println(fileContents)
takeif
1 2 3 4 5 6 val readText = File(FILE_DREAM) .takeIf { it.exists() && it.canRead() } ?.readText() println(readText)
takeUnless 和takeif是反的
takeUnless, 只有判断你给定的条件结果是 false 时,takeUnless才会返回原始接收者对象。
1 2 3 4 val result5 = File(FILE_DREAM) .takeUnless { it.isHidden } ?.readText() println(result5)
flatmap
ArrayList 转成 ArrayList
1 2 3 val flatMap = limitServiceList?.flatMap { mutableListOf(CategoryEditService(false , services = it)) }
1 2 { mutableListOf(CategoryEditService(false, services = it))} 这个是一个方法, 方法类型是transform: (T) -> Iterable<R>
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public inline fun <T, R> Iterable<T> .flatMap (transform: (T ) -> Iterable <R >) return flatMapTo(ArrayList<R>(), transform) } public inline fun <T, R, C : MutableCollection<in R> > Iterable<T> .flatMapTo (destination: C , transform: (T ) -> Iterable <R >) for (element in this ) { val list = transform(element) destination.addAll(list) } return destination }