二叉树算法思维
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1nG411x77H
TreeOperation.java打印树
Tree
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1JW411i731
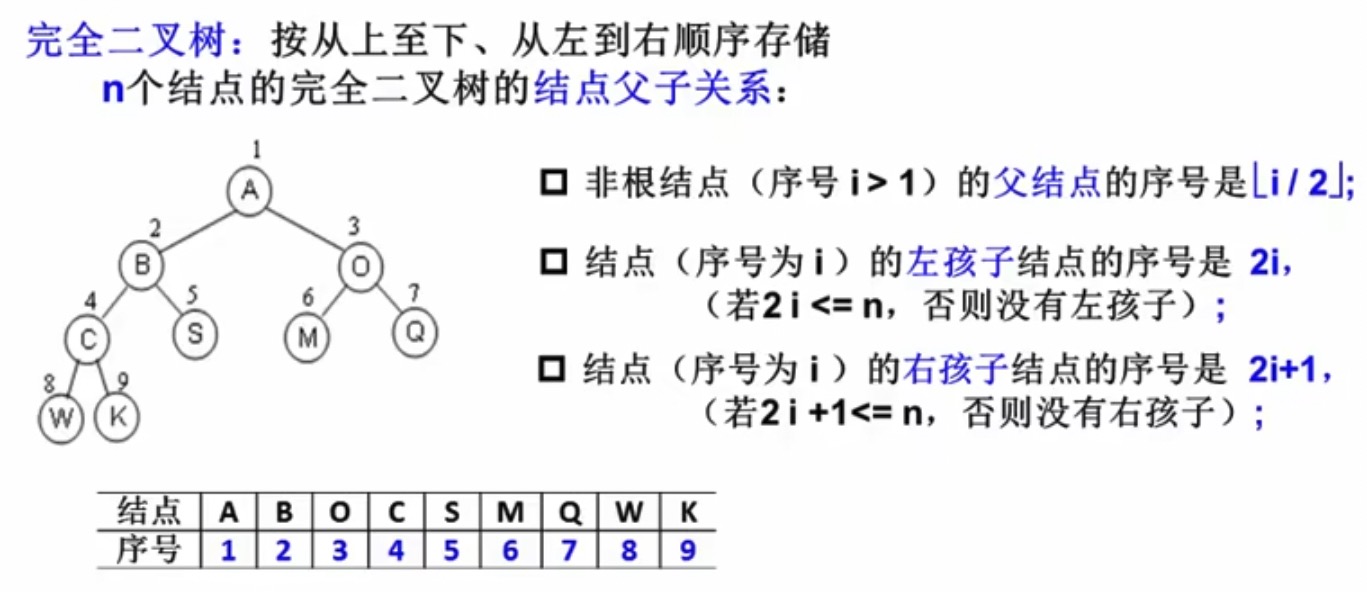
完全二叉树 数组存储方式
i 是数组下标
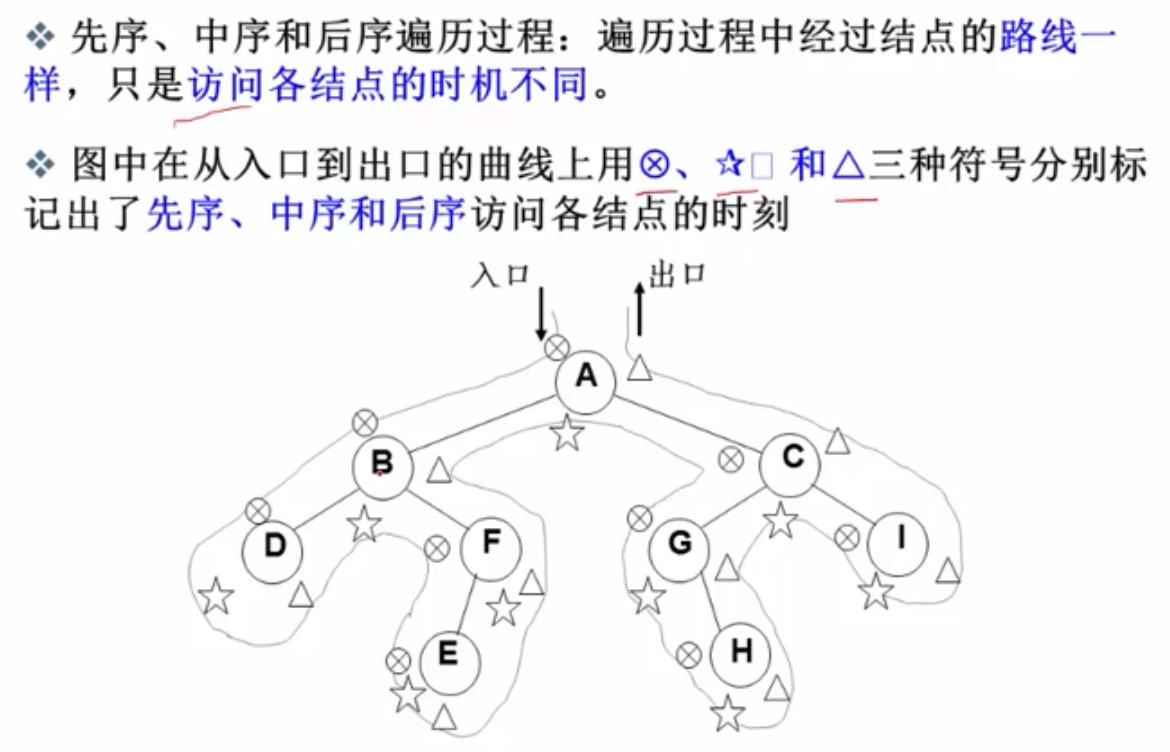
遍历
每个Node都有3次访问机会,谁先出现就代表什么序.
中间节点 在哪,代表的遍历方式
先序遍历 preorder traversal :中左右
中序遍历 inorder traversal:左中右
后序遍历 postorder traversal:左右中
https://github.com/azl397985856/leetcode/blob/master/thinkings/tree.md
preorder traversal 递归
二叉树的遍历动画
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1RR4y1j7kh
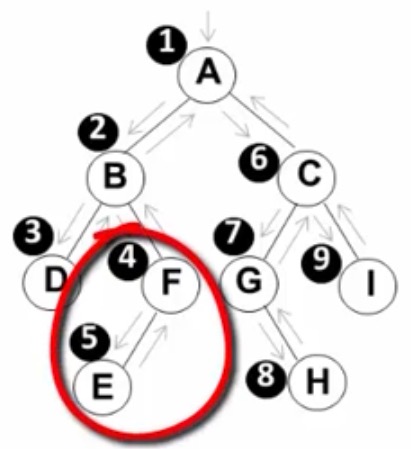
B的左边遍历完成后,开始遍历B的右子树
遍历过程
访问根节点
先序遍历其左子树
先序遍历其右子树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 void PreOrderTraversal (BinTree BT) if (BT){ printf ("%d" , BT -> Data); PreOrderTraversal(BT->Left) PreOrderTraversal(BT->Right) } }
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1JW411i731?p=34&vd_source=d4c5260002405798a57476b318eccac9
非递归 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15f4y1W7i2
构建和打印树 https://blog.nowcoder.net/n/f3799d64ed764fd49c63947d617d4cd5
https://leetcode.cn/playground/VDCGQ8Ds/
https://leetcode.cn/circle/discuss/vpcMyM/
中序遍历
层序遍历 也叫 广度优先遍历
用队列实现
while遍历纵向层数
for遍历横向
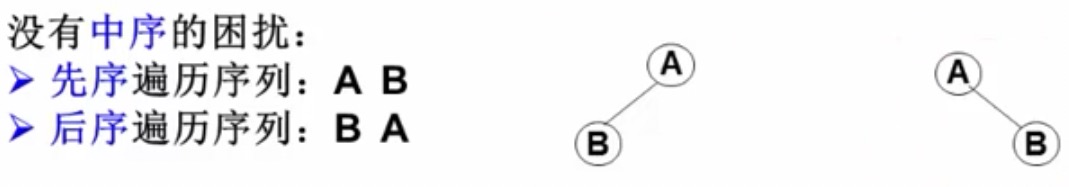
确定二叉树 必须有中序遍历,和先 后 序遍历之一
二叉搜索树
BST. Binary Search Tree
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 fun preorderTraversal (root: TreeNode ?) Int > { val linkedList = LinkedList<Int >() preTraversal(root, linkedList) return linkedList } private fun preTraversal (node: TreeNode ?, linkedList: LinkedList <Int >) if (node == null ) return linkedList.add(node.`val `) preTraversal(node.left, linkedList) preTraversal(node.right, linkedList) }
迭代
随想录
前序遍历是中左右,每次先处理的是中间节点,那么先将根节点放入栈中,然后将右孩子加入栈,再加入左孩子。
为什么要先加入 右孩子,再加入左孩子呢? 因为这样出栈的时候才是中左右的顺序。
5 4 1 2 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 fun preorderTraversal1 (root: TreeNode ?) Int > { val linkedList = LinkedList<Int >() val stack = Stack<TreeNode>() root?.let{ stack.push(it) } while (!stack.empty()) { val popNode = stack.pop() popNode.`val `.let{ linkedList.add(it) } popNode.right?.let { stack.push(it) } popNode.left?.let { stack.push(it) } } return linkedList }
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 fun inorderTraversal (root: TreeNode ?) Int > { val linkedList = LinkedList<Int >() orderRecursive(root, linkedList) return linkedList } private fun orderRecursive (node: TreeNode ?, linkedList: LinkedList <Int >) if (node == null ) return orderRecursive(node.left, linkedList) linkedList.add(node.`val `) orderRecursive(node.right, linkedList) }
迭代法
随想录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 fun inorderTraversal1 (root: TreeNode ?) Int > { val linkedList = LinkedList<Int >() if (root == null ) return linkedList val stack = Stack<TreeNode>() var node = root while (node != null || !stack.empty()) { if (node != null ) { stack.push(node) node = node.left } else { val resultNode = stack.pop() linkedList.add(resultNode.`val `) node = resultNode.right } } return linkedList }
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 fun postorderTraversal (root: TreeNode ?) Int > { val linkedList = LinkedList<Int >() recursiveTraversal(root, linkedList) return linkedList } private fun recursiveTraversal (node: TreeNode ?, linkedList: LinkedList <Int >) if (node == null ) return recursiveTraversal(node.left, linkedList) recursiveTraversal(node.right, linkedList) linkedList.add(node.`val `) }
迭代法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 fun postorderTraversal (root: TreeNode ?) Int > { var mRoot = root val resultList = LinkedList<Int >() val stack = Stack<TreeNode>() var preNode: TreeNode? = null while (mRoot != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { while (mRoot != null ) { stack.push(mRoot) mRoot = mRoot.left } mRoot = stack.pop() if (mRoot?.right == null || mRoot.right == preNode) { resultList.add(mRoot.`val `) preNode = mRoot mRoot = null } else { stack.push(mRoot) mRoot = mRoot.right } } return resultList }
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/solution/er-cha-shu-de-hou-xu-bian-li-by-leetcode-solution/ 动图
官方题解
迭代法统一写法
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/solution/dai-ma-sui-xiang-lu-che-di-chi-tou-qian-xjof1/
这个统一法还没研究,先往后学吧,地铁上看了下,其实也不难
按照顺序,下一层的放在后面.
迭代写法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 fun levelOrder (root: TreeNode ?) Int >> { val layerList = LinkedList<List<Int >>() val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size val linkedList = LinkedList<Int >() for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val headNode = queue.poll() linkedList.add(headNode.`val `) headNode.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } headNode.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } layerList.add(linkedList) } return layerList }
递归解法 递归解法一开始没理解,再看了下,思路很妙
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 fun levelOrder1 (root: TreeNode ?) Int >> { val layerList = LinkedList<LinkedList<Int >>() if (root==null ){ return layerList } val depth = 0 return recursive(layerList, root, depth) } private fun recursive (layerList: LinkedList <LinkedList <Int >>, node: TreeNode ?, depth: Int ) Int >> { if (layerList.size <= depth) { val linkedList = LinkedList<Int >() layerList.add(linkedList) } node?.`val `?.let { layerList[depth].add(it) } val mDepth = depth + 1 if (node?.left != null ) { recursive(layerList, node.left, mDepth) } if (node?.right != null ) { recursive(layerList, node.right, mDepth) } return layerList }
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/solution/er-cha-shu-de-ceng-xu-bian-li-by-leetcode-solution/
https://programmercarl.com/0102.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E5%B1%82%E5%BA%8F%E9%81%8D%E5%8E%86.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 fun levelOrderBottom (root: TreeNode ?) Int >> { val resultList = LinkedList<ArrayList<Int >>() val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size val arrayList = ArrayList<Int >() for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val headNode = queue.poll() if (headNode != null ) { arrayList.add(headNode.`val `) headNode.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } headNode.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } } resultList.addFirst(arrayList) } return resultList }
广度优先遍历 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 fun rightSideView (root: TreeNode ?) Int > { val resultList = LinkedList<Int >() val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>() if (root != null ) { queue.add(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layoutSize = queue.size for (i in 0 until layoutSize) { val headNode = queue.poll() if (i == layoutSize - 1 ) { resultList.add(headNode.`val `) } headNode?.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } headNode?.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } } return resultList }
DFS 深度优先遍历 这个DFS很妙,这次只是先理解,二刷的时候可以自己写写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solutions List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>(); public List<Integer> rightSideView (TreeNode root) dfs(root,0 ) return res; } prvidate void dfs (TreeNode root, int depth) { if (root ==null ){ return ; } if (depth == res.size()){ res.add(root.val) } depth++; dfs(root.right,depth) dfs(root.left,depth) } }
理解在官方视频中.
https://leetcode.cn/problems/binary-tree-right-side-view/solution/er-cha-shu-de-you-shi-tu-by-leetcode-solution/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 fun averageOfLevels (root: TreeNode ?) val resultList = ArrayList<Double >() val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layoutSize = queue.size var layerSum = 0. toDouble() for (i in 0 until layoutSize) { val node = queue.poll() layerSum += node.`val ` node?.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } node?.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } val average = resultList.add(layerSum * 1.00000 / layoutSize) } return resultList.toDoubleArray() }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 fun levelOrder (root: Node ?) Int >> { val result = LinkedList<ArrayList<Int >>() val queue = LinkedList<Node>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layoutSize = queue.size val layerResult = ArrayList<Int >() for (i in 0 until layoutSize) { val pollNode = queue.poll() layerResult.add(pollNode.`val `) pollNode.children.forEach { queue.offer(it) } } result.add(layerResult) } return result }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 fun largestValues (root: TreeNode ?) Int > { val answer = ArrayList<Int >() val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size var maxValue = Int .MIN_VALUE for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val pollNode = queue.poll() maxValue = pollNode.`val `.coerceAtLeast(maxValue) pollNode?.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } pollNode?.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } answer.add(maxValue) } return answer }
116. 填充每个节点的下一个右侧节点指针
一开始用这种方式,但是会提示 “超出内存限制”
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 fun connect (root: Node ?) val queue = LinkedList<Node>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } var preNode: Node?=null while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size preNode = null for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val curNode = queue.poll() preNode = curNode if (preNode != null ) { preNode.next = curNode } if (i == layerSize - 1 ) { curNode.next = null } curNode?.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } curNode?.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } } return root }
官方解法 还有另一种解法,二刷时可以研究研究
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 fun connect (root: Node ?) val queue = LinkedList<Node>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val curNode = queue.poll() if (i < layerSize - 1 ) { curNode.next = queue.peek() } curNode?.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } curNode?.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } } return root }
https://leetcode.cn/problems/populating-next-right-pointers-in-each-node/solution/tian-chong-mei-ge-jie-dian-de-xia-yi-ge-you-ce-2-4/
和116题唯一的区别,116是完美二叉树
广度优先 Breadth-First-Search 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 fun maxDepth (root: TreeNode ?) Int { val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>() var depth = 0 if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val pollNode = queue.poll() pollNode?.left?.let { queue.add(it) } pollNode?.right?.let { queue.add(it) } if (i == layerSize - 1 ) { depth++ } } } return depth }
递归 Depth First Search 这题用一个方法就可以了,遍历左右子树取最大值后 再加 1
这个其实也是先序遍历,左右中
https://programmercarl.com/0104.%E4%BA%8C%E5%8F%89%E6%A0%91%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E5%A4%A7%E6%B7%B1%E5%BA%A6.html#%E9%80%92%E5%BD%92%E6%B3%95
1 2 3 4 int leftdepth = getdepth (node->left); int rightdepth = getdepth (node->right); int depth = 1 + max (leftdepth, rightdepth); return depth;
可以看看随想录的解法,里面有回溯的过程,过程更详细
下面解法做了简化
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 fun maxDepth (root: TreeNode ?) Int { val depth = 0 if (root == null ) return depth return dfsDepth(root, depth) } private fun dfsDepth (node: TreeNode ?, depth: Int ) Int { if (node == null ) return depth val maxDepth = Math.max(dfsDepth(node.left, depth + 1 ), dfsDepth(node.right, depth + 1 )) return maxDepth }
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/solution/er-cha-shu-de-zui-da-shen-du-by-leetcode-solution/
DFS
这个DFS解法 看了官方题解答案,自己再做一次
https://leetcode.cn/problems/maximum-depth-of-n-ary-tree/solution/n-cha-shu-de-zui-da-shen-du-by-leetcode-n7qtv/
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 fun maxDepth (root: Node ?) Int { if (root == null ) return 0 var maxDepth = 0 root.children.forEach { val depth = maxDepth(it) maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, depth) } return maxDepth +1 }
BFS
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 fun maxDepth1 (root: Node ?) Int { val queue = LinkedList<Node>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } var maxDepth = 0 while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val pollNode = queue.poll() if (i == 0 ) { maxDepth++ } pollNode.children.forEach { if (it != null ) queue.offer(it) } } } return maxDepth }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 fun maxDepth1 (root: Node ?) Int { val queue = LinkedList<Node>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } var maxDepth = 0 while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size maxDepth++ for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val pollNode = queue.poll() pollNode.children.forEach { if (it != null ) queue.offer(it) } } } return maxDepth }
BFS
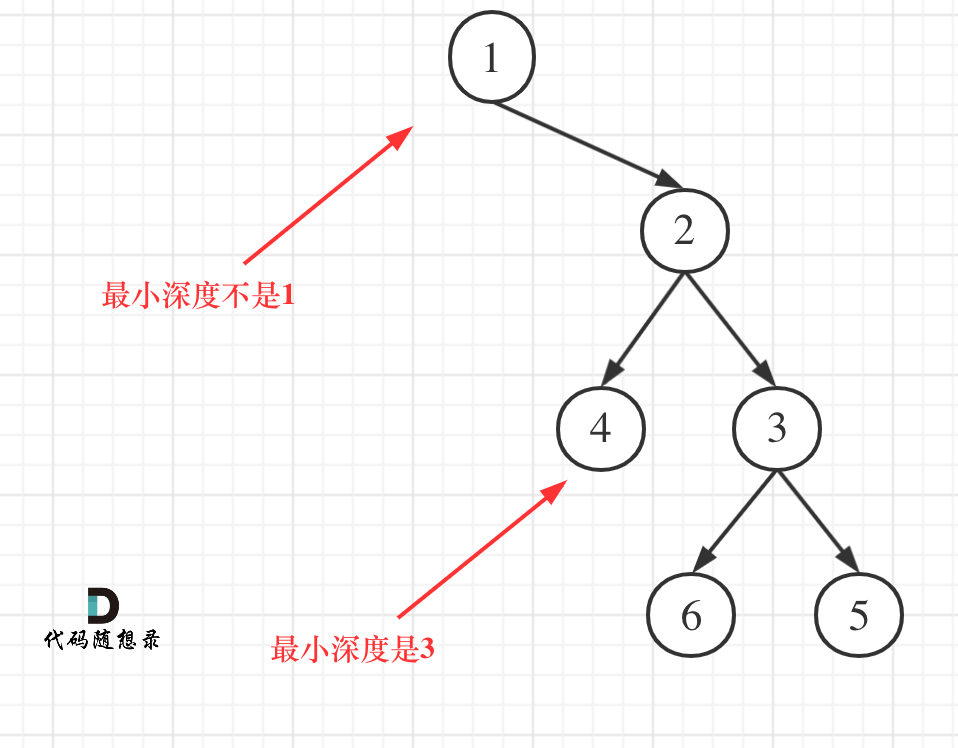
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 fun minDepth (root: TreeNode ?) Int { val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } var depth = 0 while (queue.isNotEmpty()) { val layerSize = queue.size depth++ for (i in 0 until layerSize) { val pollNode = queue.poll() if (pollNode.left == null && pollNode.right == null ) { return depth } pollNode?.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } pollNode?.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } } return depth }
官方题解看起来,更好
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/solution/er-cha-shu-de-zui-xiao-shen-du-by-leetcode-solutio/
DFS
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/solution/bfshe-dfsliang-chong-fang-shi-jie-jue-by-g4eh/
用了这个视频的解法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 fun minDepth (root: TreeNode ?) Int { if (root == null ) return 0 if (root.left != null && root.right != null ) { return Math.min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1 } else if (root.left == null ) { return minDepth(root.right) + 1 } return minDepth(root.left) + 1 }
理解了这个解法,再看官方的DFS解法,也简单明了
https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/solution/er-cha-shu-de-zui-xiao-shen-du-by-leetcode-solutio/
递归
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 fun invertTree (root: TreeNode ?) if (root == null ) return null swapNode(root) invertTree(root.left) invertTree(root.right) return root } private fun swapNode (node: TreeNode ?) val temp = node?.left node?.left = node?.right node?.right = temp }
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public TreeNode invertTree(TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) return null ; invertTree(root.left); TreeNode temp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = temp; invertTree(root.left); return root; }
————————————————https://blog.csdn.net/xsybg/article/details/122687168
注意两个递归调用的参数都是root.left, 因为在第二步是交换root的左右孩子,所以在第三步要处理的右孩子其实已经变成了root的左孩子,是不是很有趣?https://blog.csdn.net/xsybg/article/details/122687168
根据下面打印
4的坐子树中的1,3交换了两次, 6,9一次都没交换
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 4 / \ 2 7 / \ / \ 1 3 6 9 node 4 4 / \ 2 7 / \ / \ 1 3 6 9 node 2 4 / \ 2 7 / \ / \ 1 3 6 9 node 1 4 / \ 2 7 / \ / \ 1 3 6 9 node 1 4 / \ 2 7 / \ / \ 3 1 6 9 node 2 4 / \ 7 2 / \ / \ 6 9 3 1 node 3 4 / \ 7 2 / \ / \ 6 9 3 1 node 3 4 / \ 7 2 / \ / \ 6 9 1 3
广度优先遍历(层序遍历) 遍历左右节点就可以.然后交换就可以了
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 fun invertTree1 (root: TreeNode ?) val queue = LinkedList<TreeNode>() if (root != null ) { queue.offer(root) } while (queue.isNotEmpty()){ val layerSize = queue.size for (i in 0 until layerSize){ val pollNode = queue.poll() swapNode(pollNode) pollNode.left?.let { queue.offer(it) } pollNode.right?.let { queue.offer(it) } } } return root }