也可以参考一起https://jonblog.site/2024/05/31/reflection/ https://jonblog.site/2024/05/28/designpattern-proxy/ https://jonblog.site/2024/06/06/annotation/
Static Proxy 编译的时候就已经存在
Compile-Time Creation: Static proxies are created at compile time, meaning you need to write the proxy class manually.
Tight Coupling: Since you need to write the proxy class, there’s a tighter coupling between the proxy and the original class.
Use Cases: Often used for simple scenarios where you need to add a specific behavior to a method call.
Separate Proxy Class: You have to create a separate class for the proxy which implements the same interface as the target class.
Java implement 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public interface ZyxInterface { void sayHello (String name) ; } public class ZhangYuXin implements ZyxInterface { @Override public void sayHello (String name) { System.out.println("Hello from zyx " + name); } }
代理类
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class ZhangYuXinProxy implements ZyxInterface { private ZhangYuXin zhangYuXin; public ZhangYuXinProxy (ZhangYuXin zhangYuXin) { this .zhangYuXin = zhangYuXin; } @Override public void sayHello (String name) { System.out.println("拍电影前的准备工作" ); zhangYuXin.sayHello(name); System.out.println("拍电影后的收尾工作" ); } }
1 2 3 ZhangYuXin zyxHello = new ZhangYuXin ();ZhangYuXinProxy zhangYuXin = new ZhangYuXinProxy (zyxHello);zhangYuXin.sayHello("hello" );
运行结果
拍电影前的准备工作
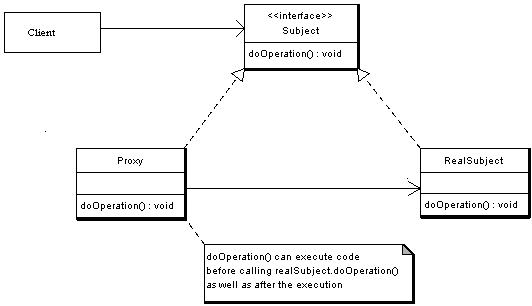
UML
代理模式
代理类与委托类有同样的接口
代理类主要负责为委托类预处理消息、过滤消息、把消息转发给委托类,以及事后处理消息等。
一个代理类的对象与一个委托类的对象关联,代理类的对象本身并不真正实现服务,而是通过调用委托类的对象的相关方法,来提供特定的服务。
Dynamic Proxy 通过反射机制生成的代理对象
Dynamic proxies in Java are created at runtime. They use reflection and the java.lang.reflect.Proxy class along with the InvocationHandler interface to handle method invocations.
Key Characteristics:
Runtime Creation: Dynamic proxies are created at runtime, which means you don’t need to write separate classes for proxies.
Flexibility: Since they are created at runtime, they can be more flexible and can easily adapt to changes.
Use Cases: Commonly used in frameworks like Spring AOP for cross-cutting concerns (e.g., logging, transaction management).
No Implementation Class Needed: You don’t need to create a separate class for the proxy; you just need to provide an implementation for the InvocationHandler.
Summary
Dynamic Proxy:
Static Proxy:
Dynamic proxy implementation 生成的动态代理Class文件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 public class DoSomeThingDynamic { Object object; public DoSomeThingDynamic (Object object) { this .object = object; } public <T> T create (final Class<T> say) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(say.getClassLoader(), new Class <?>[]{say}, new InvocationHandler () { @Override public Object invoke (Object o, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("拍电影前的准备工作" ); Object result = method.invoke(object, args); System.out.println("拍电影后的收尾工作" ); return result; } } ); } }
call from client 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 DoSomeThingDynamic say1 = new DoSomeThingDynamic (zyxHello);ZyxInterface zyxProxy = say1.create(ZyxInterface.class);zyxProxy.sayHello("John" ); System.out.println("---------------------\n" ); BinBin binBye = new BinBin ();DoSomeThingDynamic say2 = new DoSomeThingDynamic (binBye);BinInterface bbProxy = say2.create(BinInterface.class);bbProxy.sayBye(); byte [] classFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass("BinInterface$0" , new Class []{ZyxInterface.class});try { FileOutputStream out = new FileOutputStream ( "BinInterface$0.class" ); out.write(classFile); out.flush(); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }
BinInterface$0.class
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public final class BinInterface$1 extends Proxy implements ZyxInterface { private static Method m1; private static Method m3; private static Method m2; private static Method m0; public BinInterface$1 (InvocationHandler var1) throws { super (var1); } public final boolean equals (Object var1) throws { try { return (Boolean)super .h.invoke(this , m1, new Object []{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException (var4); } } public final void sayHello (String var1) throws { try { super .h.invoke(this , m3, new Object []{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException (var4); } } public final String toString () throws { try { return (String)super .h.invoke(this , m2, (Object[])null ); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException (var3); } } public final int hashCode () throws { try { return (Integer)super .h.invoke(this , m0, (Object[])null ); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var2) { throw var2; } catch (Throwable var3) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException (var3); } } static { try { m1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object" ).getMethod("equals" , Class.forName("java.lang.Object" )); m3 = Class.forName("pattern.proxy.xiangxue.ZyxInterface" ).getMethod("sayHello" , Class.forName("java.lang.String" )); m2 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object" ).getMethod("toString" ); m0 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object" ).getMethod("hashCode" ); } catch (NoSuchMethodException var2) { throw new NoSuchMethodError (var2.getMessage()); } catch (ClassNotFoundException var3) { throw new NoClassDefFoundError (var3.getMessage()); } } }
运行结果
拍电影前的准备工作
拍电影前的准备工作
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ib4y1f7S1?p=10&spm_id_from=pageDriver https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1uQ4y1Z7gA?p=23 https://juejin.cn/post/6844903520919879694 https://juejin.cn/post/6844903978342301709 https://time.geekbang.org/column/article/201823
Dynamic proxy principle
sequenceDiagram
DynamicProxyTest->>BinInterface$0 : invoke sayHello("hello")
BinInterface$0 ->> InvocationHandler : h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[]{var1})
Note right of InvocationHandler : 传参调用到InvocationHandler的invoke
InvocationHandler ->> ZhangYuXin: method.invoke(object, args)
Note right of ZhangYuXin : 类似于 object.method(arg)
我们下面 bbProxy.sayBye(); 调用开始分析整个流程
bbProxy 是生成的代理类对象,调用后进入到代理类方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public final void sayHello (String var1) throws { try { super .h.invoke(this , m3, new Object []{var1}); } catch (RuntimeException | Error var3) { throw var3; } catch (Throwable var4) { throw new UndeclaredThrowableException (var4); } }
调用 super.h.invoke(this, m3, new Object[]{var1}); super.h 是调用public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)传进来的new InvocationHandler() 最终调用到
cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h} 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 private static final Class<?>[] constructorParams = { InvocationHandler.class }; public static Object newProxyInstance (ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h) { final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams); return cons.newInstance(new Object []{h}); }
cl.getConstructor(constructorParams) 指定的是 InvocationHandler类型的构造方法, 也就是
1 2 3 4 protected Proxy (InvocationHandler h) { Objects.requireNonNull(h); this .h = h; }
正常流程
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 @Override public Object invoke (Object o, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { System.out.println("拍电影前的准备工作" ); Object result = method.invoke(object, args); System.out.println("拍电影后的收尾工作" ); return result; }
Object result = method.invoke(object, args); 开始调用代理类的方法。
1 2 3 4 5 6 @Override public void sayHello (String name) { System.out.println("拍电影前的准备工作" ); zhangYuXin.sayHello(name); System.out.println("拍电影后的收尾工作" ); }
Simulate Jdk this video write code simulate JDK dynamic proxy
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1Ve411o7WM
simple 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class ProxyDog implements Target { InvocationHandler h; public ProxyDog (InvocationHandler h) { this .h = h; } @Override public void eat () { h.invoke(); } @Override public void drink () { h.invoke(); } } ProxyDog proxyDog = new ProxyDog (new InvocationHandler () { @Override public void invoke () { System.out.println("before" ); new TargetDog ().eat(); } }); proxyDog.eat(); proxyDog.drink();
这种方式 调用 drink()后,没法区分,调用drink(), 还是调用了eat()
simulate jdk 模拟jdk动态代理,InvocationHandler方法是自己的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 interface InvocationHandler { void invoke (Method method,Object[] args) ; } public class ProxyDog implements Target { InvocationHandler h; public ProxyDog (InvocationHandler h) { this .h = h; } static Method eat; static Method drink; static { try { eat = Target.class.getMethod("eat" ); drink = Target.class.getMethod("drink" ); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } @Override public void eat () { h.invoke(eat, new Object [0 ]); } @Override public void drink () { h.invoke(drink, new Object [0 ]); } } ProxyDog proxyDog = new ProxyDog (new InvocationHandler () { @Override public void invoke (Method method, Object[] args) { System.out.println("before" ); try { method.invoke(new TargetDog (),args); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } }); proxyDog.eat(); proxyDog.drink();
simulate with jdk InvocationHandler 下面的做法使用Jdk自带的InvocationHandler
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 public class ProxyDog implements Target { InvocationHandler h; public ProxyDog (InvocationHandler h) { this .h = h; } static Method eat; static Method drink; static { try { eat = Target.class.getMethod("eat" ); drink = Target.class.getMethod("drink" ); } catch (NoSuchMethodException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } @Override public void eat () { try { h.invoke(this ,eat, new Object [0 ]); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } @Override public void drink () { try { h.invoke(this ,drink, new Object [0 ]); } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } } ProxyDog proxyDog = new ProxyDog (new InvocationHandler () { @Override public Object invoke (Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) { System.out.println("before" ); try { return method.invoke(new TargetDog (), args); } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } catch (InvocationTargetException e) { throw new RuntimeException (e); } } }); proxyDog.eat(); proxyDog.drink();
从上面可以看到,Method eat = Target.class.getMethod(“eat”); class中的Method,可以作为参数传递。
Dynamic Constructor analysis final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
kotlin 委托的作用 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 interface Base { fun print () } class BaseImpl (val x: Int ) : Base { override fun print () } class Derived (b: Base) : Base by b fun main () val b = BaseImpl(10 ) Derived(b).print() }
反编译后的代码
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 package test;public final class BaseImpl implements Base { private final int x; public void print () { int var1 = this .x; System.out.print(var1); } public final int getX () { return this .x; } public BaseImpl (int x) { this .x = x; } } public final class Derived implements Base { private final Base $$delegate_0; public Derived (@NotNull Base b) { Intrinsics.checkNotNullParameter(b, "b" ); super (); this .$$delegate_0 = b; } public void print () { this .$$delegate_0.print(); } }