Bitmap
Studying bitmap involves understanding how bitmap images are represented, stored, and manipulated. Here’s a guide to help you get started:
Understanding Bitmap Basics
- Definition: A bitmap (or raster graphic) is a type of digital image composed of a matrix of dots (pixels). Each pixel represents a single point in the image and has its own color value.
- Resolution: Bitmap images have a resolution defined by the number of pixels horizontally and vertically. Higher resolution means more detail.
- Color Depth: This indicates the number of bits used to represent the color of each pixel. Common color depths are 8-bit (256 colors), 16-bit, 24-bit (true color), and 32-bit (true color with alpha channel for transparency).
Steps to Study Bitmap
- Learn the File Formats:
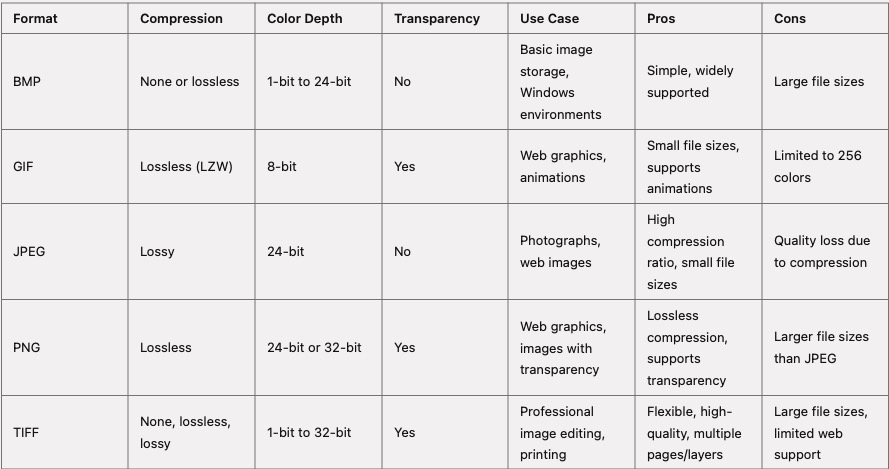
• Study different bitmap file formats such as BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG, and TIFF.
• Understand how these formats store pixel data, color information, and metadata. - Get Familiar with Bitmap Data Structure:
• Learn how bitmap images are stored in memory or files. For example, a BMP file typically starts with a header that contains information about the image’s size, color depth, and compression method. - Programming with Bitmaps:
• Practice reading and writing bitmap files using a programming language like Python, C++, or Java.
• Use libraries such as PIL/Pillow in Python or OpenCV to manipulate bitmap images. - Manipulating Bitmap Images:
• Learn common image processing techniques such as resizing, cropping, rotating, and color adjustments.
• Explore algorithms for more advanced processing like filtering, edge detection, and transformations. - Study Compression Techniques:
• Understand lossless (e.g., PNG) and lossy (e.g., JPEG) compression methods and how they affect image quality and file size. - Use Image Editing Software:
• Experiment with bitmap images using tools lik
Bitmap file formats differ
Bitmap file formats differ in how they store image data, their support for transparency, compression methods, and intended use cases. Here’s an overview of the most common bitmap file formats:
BMP (Bitmap)
1 | • File Extension: .bmp |
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format)
1 | • File Extension: .gif |
JPEG (Joint Photographic Experts Group)
1 | • File Extension: .jpg, .jpeg |
PNG (Portable Network Graphics)
1 | • File Extension: .png |
TIFF (Tagged Image File Format)
1 | • File Extension: .tif, .tiff |
Bitmap
https://noteforme.github.io/2024/06/28/bitmap/