os_mit
MIT6.S081
GitHub - YukunJ/xv6-operating-system: XV6 - MIT 6.s081 operating system Fall 2020 version
环境配置
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/449687883
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/442656932
MIT 6.S081: Operating System Engineering - CS自学指南
这几位教授还专门写了一本教程,详细讲解了 xv6 的设计思想和实现细节。
这门课的讲授也很有意思,老师会带着学生依照 xv6 的源代码去理解操作系统的众多机制和设计细节,而不是停留于理论知识。每周都会有一个 lab,让你在 xv6 上增加一些新的机制和特性,非常注重学生动手能力的培养。整个学期一共有 11 个 lab,让你全方位地深刻理解操作系统的每个部分,非常有成就感。而且所有的lab都有着非常完善的测试框架,有的测试代码甚至上千行,让人不得不佩服 MIT 的几位教授为了教好这门课所付出的心血。
这门课的后半程会讲授操作系统领域的多篇经典论文,涉及文件系统、系统安全、网络、虚拟化等等多个主题,让你有机会接触到学界最前沿的研究方向。
课程资源
- 课程网站:https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.828/2021/schedule.html
- 课程视频: - YouTube,每节课的链接详见课程网站
- 课程视频翻译文档:简介 | MIT6.S081
- 课程教材:https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.828/2021/xv6/book-riscv-rev2.pdf
- 课程作业:https://pdos.csail.mit.edu/6.828/2021/schedule.html,11个lab,具体要求详见课程网站
6.S081 Fall 2020 Lecture 1: Introduction and Examples - YouTube
If you want to know more about page tables, and how the OS handles memory, we encourage you to take a computer organization course after completing this specialization.
https://www.coursera.org/learn/pointers-arrays-recursion/supplement/QuCc7/string-literals
https://hub.docker.com/r/calvinhaynes412/mit6.s081
config docker
https://docs.docker.com/reference/cli/docker/container/
2021
1 | |
方法
VS Code 已安装扩展 Dev Containers(扩展市场搜索安装)。
在 VS Code 里附着
打开 VS Code。
打开 命令面板:⌘⇧P(Ctrl+Shift+P)。
选择, show and run command
输入并选择:Dev Containers: Attach to Running Container…
在弹出的列表里选择你的容器(例如 mit6.s081)。
VS Code 会自动打开一个新窗口,状态栏左下角会显示
Dev Container: <容器名>。
2020
1 | |
“/Users/m/Documents/MIT6S081/20labs” is local directory in mac
本地用户浏览器访问 http://localhost:8848/ 密码: mit6s081.
服务器端用户浏览器访问http://<服务器公网ip>:8848/ 密码: mit6s081.
https://docs.docker.com/reference/cli/docker/container/
Docker container
run home
1 | |
https://hub.docker.com/search?q=s081&architecture=amd64
run office
1 | |
https://hub.docker.com/r/calvinhaynes412/mit6.s081
https://hub.docker.com/search?q=s081&architecture=amd64
1 | |
当前主机 / docker容器内的目录
lab note
排版差但是准确
https://th0ar.gitbooks.io/xv6-chinese/content/content/chapter0.html
排版好但是代码显示有误
MIT 6.S081 Lecture Notes - Xiao Fan’s Personal Page
code
可以看看berkeley的cs61c课程,做完与riscv相关的两个lab和一个project,你就会对riscv非常了解了
Video
阿苏EEer
process
1 | |
why child cannot reach printf(“execute: after\n”)
Lab1 pipe
一个管道,parent 和child 可以操作。
如果parent , child 都要写入和读取 ,那么就建立 两个管道,一个读取,一个写入。
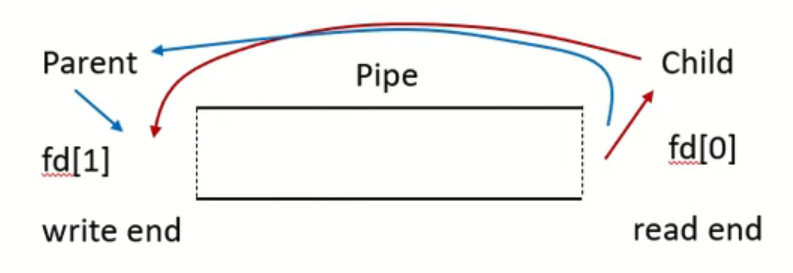
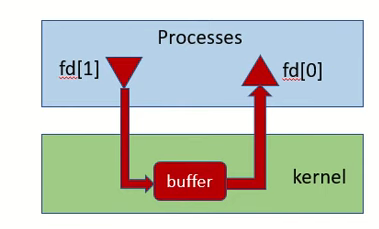
OS24 - Pipes | Interprocess Communication - YouTube
Lab2系统调用
lab code
MIT 6.1810 操作系统 Lab全解 - Cubane的专栏 - 掘金
Mit6.S081学习笔记
https://tarplkpqsm.feishu.cn/docs/doccnoBgv1TQlj4ZtVnP0hNRETd
系统调用流程
[mit6.s081]Lab2: System calls | 系统调用_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
MIT6.s081操作系统: lec6 trap陷阱机制 走进system call的前世今生 课程导读和源码浅析_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
讲解详细的调用流程
$ trace 32 grep hello README
1 | |
32 = 2的5次方 , 所以是追踪 read系统调用。从README文件中找hello字符串。
System call tracing
In the first example above, trace invokes grep tracing just the read system call. The 32 is 1<<SYS_read. In the second example, trace runs grep while tracing all system calls; the 2147483647 has all 31 low bits set. In the third example, the program isn’t traced, so no trace output is printed. In the fourth example, the fork system calls of all the descendants of the forkforkfork test in usertests are being traced. Your solution is correct if your program behaves as shown above (though the process IDs may be different).
Some hints:
Add $U/_trace to UPROGS in Makefile
1
2
3
4
5
6
7UPROGS=\
$U/_cat\
$U/_usertests\
$U/_grind\
$U/_wc\
$U/_zombie\
$U/_trace\Run make qemu and you will see that the compiler cannot compile user/trace.c, because the user-space stubs for the system call don’t exist yet: add a prototype for the system call to user/user.h, a stub to user/usys.pl, and a syscall number to kernel/syscall.h. The Makefile invokes the perl script user/usys.pl, which produces user/usys.S, the actual system call stubs, which use the RISC-V ecall instruction to transition to the kernel. Once you fix the compilation issues, run trace 32 grep hello README; it will fail because you haven’t implemented the system call in the kernel yet.
Add a sys_trace() function in kernel/sysproc.c that implements the new system call by remembering its argument in a new variable in the proc structure (see kernel/proc.h). The functions to retrieve system call arguments from user space are in kernel/syscall.c, and you can see examples of their use in kernel/sysproc.c.
Modify fork() (see kernel/proc.c) to copy the trace mask from the parent to the child process.
Modify the syscall() function in kernel/syscall.c to print the trace output. You will need to add an array of syscall names to index into.
Sysinfo
添加系统调用的代码步骤可以看 , syscall分支 sysinfo syscall Your Name 10/15/25, 6:23 PM 这个提交
Lab3
Gdb debug
在一个窗口执行make qemu-gdb
1 | |
在另一个窗口执行
1 | |
MIT 6.S081 xv6调试不完全指北 - KatyuMarisa - 博客园
如果找不到问题,还是报错先
1 | |
Speed up system calls (easy)
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/429304672
一开始报出这个错误,修改后还是,make clean 之后就好了
usertrap(): unexpected scause 0x000000000000000d pid=4
sepc=0x0000000000000480 stval=0x0000003fffffd000
Lab4
汇编debug,按enter 键